|
Do you know how to produce high-precision gears and racksIn response to the problem of high processing costs for high-precision large modulus gear racks using specialized cutting tools and specialized machine tools, a universal angle head on a CNC milling machine is used to improve the processing method. During the processing, a measuring rod is used instead of a template for random measurement, effectively ensuring the machining accuracy of tooth profile and pitch. The precision of the teeth produced by Taiwen T-win is high, and the standard grinding accuracy can reach DIN6 level, with a straightness of less than 0.03. We can customize according to the gear drawings or provide technical drawing support.
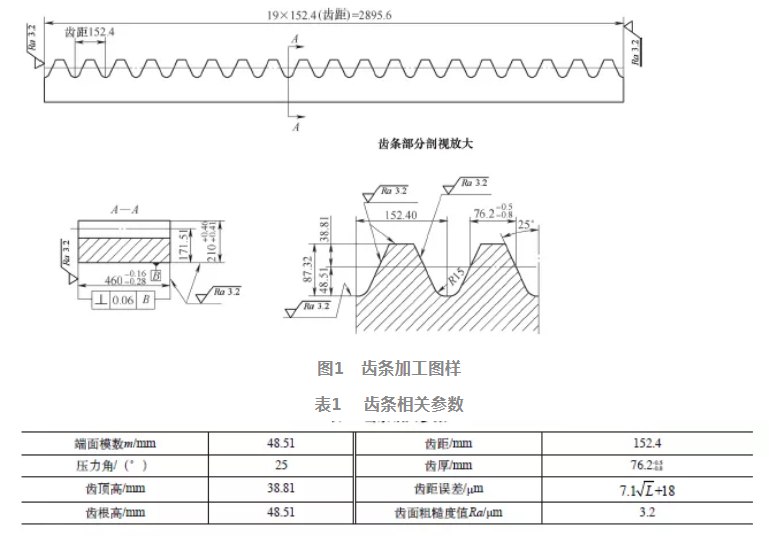
Process parameters of the workpiece The material of the workpiece is 42CrMo, with a hardness of 248~302HBW and a tensile strength of 850MPa. The corresponding technical parameters of the rack are shown in Table 1, where L is the distance (mm) between any two teeth on the rack.
The machining difficulties and schemes of gear racks From Figure 1, it can be seen that the outer dimensions of the gear rack are 2895.6mm x 460mm x 210mm, which is a typical slender part. Directly processing the gear shape from the forging blank is difficult to control the deformation, which requires a reasonable process sequence and effective clamping methods for workpiece processing; The requirements for tooth thickness tolerance and tooth pitch error of the rack are very small, and the cumulative error of tooth pitch within the full length range does not exceed 0.4mm. If forming milling cutters or hobbing cutters are used for processing, as the processing continues, the tools will inevitably experience certain wear, which cannot guarantee the accuracy of tooth pitch and will also lead to an increasing cumulative error of tooth pitch, which cannot meet the requirements of the rack's use. Taking into account the above factors and the equipment situation of our unit, the manufacturing process for the gear rack is formulated as follows: forging blank → rough machining → quenching and tempering → first semi precision machining → manual aging → second semi precision machining → natural aging → precision machining → assembly and splicing of each gear rack. Manufacturing process methods and control measures for gear racks (1) Rough machining is the process of converting raw materials into semi-finished products. In order to reduce costs and improve processing efficiency, it is arranged on the Skoda W200H digital display floor boring machine in the Czech Republic, using φ 200mm cutter head φ 315mm three sided milling cutter and φ Process with a 25mm cutterhead. First, adopt the φ Process the six sides of the gear rack with a 200mm cutter head, leaving a 10mm machining allowance on each side, and then use a universal angle head for machining φ 315mm three sided milling cutter, make a straight groove along the tooth profile, and then stand the workpiece on the side φ The 25mm cutterhead is processed into tooth profile surfaces on both sides in a zigzag pattern, with a 10mm machining allowance on each surface. This can quickly remove most of the machining allowance, compared to using a single tool φ The efficiency of rough milling of tooth slots with a 25mm cutter head has increased by nearly three times. (2) After the first semi precision machining of the gear rack, it was subjected to quenching and tempering treatment and returned to a 3m × 8m CNC gantry milling machine for semi precision machining. Place the workpiece flat on the workbench for two clamping processes. During the alignment process, it was found that each rack had deformation towards the concave center of the tooth side, with a deformation amount of 3-5mm. This is mainly caused by the removal of a large amount of machining on the tooth profile side during the rough machining stage. After considering the machining allowance evenly, semi precision machining of the outer profile and tooth profile is carried out, with a 5mm allowance left on each surface, and manual aging is carried out in the next sequence. (3) After artificial aging, the residual stress inside the second semi precision machining of the gear rack will be fully released. The main processing content of this sequence includes semi precision machining of tooth profiles, contour surfaces, and machining of various connecting holes. On the CNC gantry milling machine, follow the clamping method shown in Figure 2 and use a universal angle head φ The tooth profile is processed with a 250mm right angle cutterhead, divided into 2-3 passes, leaving a 1mm machining allowance on one side. Then, the workpiece is turned 180 °, and the bottom surface is machined to a 1mm machining allowance. The next step is natural aging for 5 days. The semi precision machining process can process gear racks in groups on the same machine tool, which can shorten the overall machining cycle. (4) The control method for precision machining: The equipment and processing method used in this process are the same as those in the previous sequence, but the difference lies in the control of the machining accuracy of the gear rack. Firstly, clamp the workpiece with its bottom facing the spindle of the machine tool, and place an equal height shim underneath. After alignment, gently clamp it and machine the bottom to a machining allowance of 0.3mm. Then, flip the workpiece 180 ° and place it on the equal height shim to machine the tooth profile. First, machine the tooth top surface to the size shown in the drawing. Due to the high requirements for tooth thickness and pitch accuracy, a measuring rod is used to control the accuracy of tooth profile during precision machining. When selecting the diameter of the measuring rod, the contact point between the outer circle of the measuring rod and the tooth profile should fall on the dividing line and its nearby position. Generally, the selection is based on the diameter of the measuring rod D=(1.68-1.72) m, where m is the end face modulus (mm). After calculation, rounding is adopted φ Measure with a measuring rod of (80 ± 0.01) mm. The specific control method is to draw the distance h between the highest point of the standard measuring rod and the tooth top according to the dimensions required in the drawing, as shown in Figure 3. During the machining process, first machine one side of all teeth to meet the requirements of the drawing, then place the measuring rod in the first tooth valley and use a dial gauge to measure the actual distance h ′ between the measuring rod and the tooth top. The difference between h ′ and h is Δ h. So the machining allowance A along the length direction of the gear rack on the cutterhead can be calculated according to the formula A=2 Δ Htan25 ° for calculation. After finishing the first tooth, the machine tool slide travels 152.4mm along the length direction of the rack to process the second tooth, sequentially processing each tooth and its length dimension. The tooth surface is processed in three passes, and then the root of the tooth is cleaned using an R15 ball cutter. After the tooth profile machining is completed, the workpiece is flipped over to remove the machining allowance for thickness and width, and then transferred to the next sequence for assembly. epilogue By adopting reasonable process methods, the machining accuracy of the rack is well ensured, and the deformation of each machining surface of the rack is ensured to be within 0.1mm. The surface roughness value Ra is controlled at 1.6 μ Within m. During the tooth profile machining process, a measuring rod is used instead of a tooth profile pitch template for measurement, effectively ensuring the accuracy of the tooth profile. The cumulative error of the full length tooth pitch is between 0.10 and 0.15mm. This provides a certain reference for the processing of similar products in the future. |